6/06/2010 @ 2:05 PM
Linear Relations
In this unit, you will learn about slope, slope as a rate of change, direct variation, and partial variation.First, we learned about slope. Slope is the steepness of a line, and it is measured by its slope. The slope of the straight line is the ratio of the rise to the run between both points.
The equation for slope is m = rise/run (rise over run), where m is slope.
The picture above shows an example of slope. To find the slope of a line, you find two points on the line, and imagine a triangle. Then, depending on how you think, you would move 2 times to the right, since the formula is m = rise/run. After that, you do the same thing, but move upwards 4 times instead of moving right, since we are trying to find the slope.
Rise = 4 Run = 2
m = rise/run
m = 4/2
m = 2/1
The run is horizontal (x-axis), and the rise is vertical (y-axis).
If the line is moving upwards/increasing, the slope is positive.
If the line is moving downwards/decreasing, the slope is negative.
TIP: In some cases, the line is a straight line with no rise or no run.
If the rise is 0 and the run is a #, the slope is always 0. EXAMPLE: 0/#
If the rise is a # and the run is 0, the slope is undefined. EXAMPLE: #/0
Therefore, horizontal lines have a slope of 0 (no rise), and vertical lines have a slope that is undefined (no run, cannot divide by zero).Another thing we learned was slope as a rate of change. A rate of change compares the change in one quantity relative to a change in another quantity.
Unlike slope, though, a rate of change is expressed in units! For example, km/h.
Basically, slope and rate of change are the same thing.
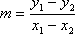 The formula for rate of change is the change in dependent variable divided by the change in independent variable. So, the formula would be y2 - y1/ x2 - x1.
The formula for rate of change is the change in dependent variable divided by the change in independent variable. So, the formula would be y2 - y1/ x2 - x1.EXAMPLES: Loujain runs 25 km in 5 hours. What is her speed?
= 25/5
=5km/h
Sarah has a race with Sohyun. Sarah ran 30km in 3 hours, and Sohyun ran 36km in 6 hours. Who ran more?
Sarah- =30/3
=10 km/h
Sohyun- = 36/6
= 6 km/h
Sarah ran more.
Direct variation is the relationship between 2 variables in which one variable is a constant multiple of the other. Some characteristics of direct variation is how the graph will always be linear (straight line), the graph will always intercept the y-axis at the origin, and the equation for direct variation is always y = mx.
EXAMPLE: y=2x
D=5t
C=25h
H=10t
Partial variation is when the relationship between two variables have both a fixed and variable amount. Some characteristics of partial variation is how the fixed variable does not change- although the variable value changes, the graph intersects below or above the y-axis, the equation is always y = mx + b, and the line on a partial variation graph never passes through the origin.
EXAMPLE: C = 2.00 + 0.50n
T = 232 + 3n
y = 3.5x + 3
y = 0.2x + 5
TIP: the m (slope) and b (fixed cost) are constants.
m represents the constant of variation (multiple).
b represents the fixed, initial value.
Labels: Lessons
back to the top.
